- HOME
- Product Information
- Specially & Perfomance Materials
- Polymer beads
- GANZPEARL Spherical polymer beads
Polymer beads
GANZPEARLS are spherical, organic particles which are obtained by means of the polymerization of monomers, primarily methacrylic esters, styrene, silicone and urethane.
When compared with inorganic particles, GANZPEARL boasts lower specific gravity, higher transparency, and greater compatibility and dispersibility in relation to resins.
Product development by Use
Cosmetics
For the manufacture of cosmetics, we produce a highly refined grade that is low in impurities and residual monomer.
We provide fine particles of polymethyl methacrylate, polystyrene, silicone, and polyurethane.
When added to foundation, lotions etc, it improves feel and spreadability.
We also have types such as those shown below as characteristic grades.
- Readily water disperse type
- Porous type
- Non-spherical type
- Soft type (acrylic, silicone, polyurethane)
Light diffusing agents
Resin blending type
"By utilizing the difference between the refractive index with the matrix resin, refractes light at the interface and shows light scattering effect.
Excellent dispersion on the resin and heat resistance (meaning thermal decomposition and thermal yellowing)."
We can modify the following property.
- Refractive index control (1,410-1,590)
- Average particle size control (2~100μm)
- Particle size distribution (control of fine and coarse powder)
- Particle construction control (porous, core and shell multilayer construction)
Film coating type
Coating GANZPEARL to PET film provide high luminosity light diffusion film.
Sophisticated cross-linking for advanced varnish dispersibility.
Additive for coating
Matte or patterned finish
It's possible to give the design (matting and patterning) by adding to paint.Excellent solvent resistance and dispersion performance to the paint.
There are general hard type (PMMA) and soft type which is excellent scratch resistance (PBMA and polyurethane).
There are also a porous type which is excellent matting in addition to general true spherical type.
For the case that is added in water-based paint, an arrangement in the type of wet powder(moisture content 10~20 percent) is possible.
Film additive agents
Anti-blocking agent for olefin film
This is a grade listed in Appendix 1 and Appendix 2 (Additives) found within the positive list program for food utensil and container packaging run by Japan's Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare.
Excellent dispersion on the resin and heat resistance (meaning thermal decomposition and thermal yellowing).
There are also grades wherein die drool (which is a problem during the membrane production of polyethylene film) occurs infrequently.
Pore-adding agent/pore-forming agent
These can be used as pore-forming agents which adds small cavities (pores) to molded items by mixing them and undertaking a high-temperature calcination process.
It offers excellent thermal decomposability and is characterized by low levels of residue after the calcination process.
Small cavities (pores) with stable sizes can be added since particle sizes are uniform.
-
Alumina grinding stone
-

Surface of grinding stone
Technical Information
Various physical properties can be controlled.
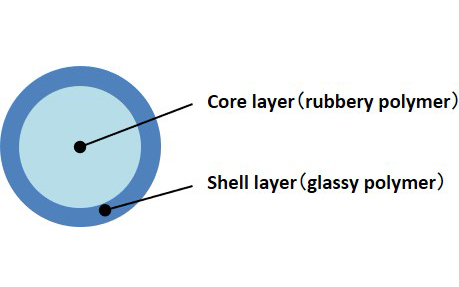
Shape and structure
- Synthesis of particles with shape characteristics is also possible.
- Synthesis is also possible for core-shell structure particles.
-
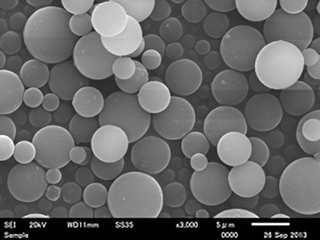
General grade
- Spherical and smooth surface.
- Possible to add slippery properties.
-

Porous grade
- Porous shape with unevenness in the surface.
- It is possible to improve adhesion in relation to resins thanks to the anchoring effect provided.
- Customers can expect improvements in terms of optical scattering properties as a result of the uneven structure.
- Provides a soft feel that is derived from the rubber layer.
- Structure featuring easy tracking on changes such as stretching.
- Conjugation with inorganic particles is also possible.
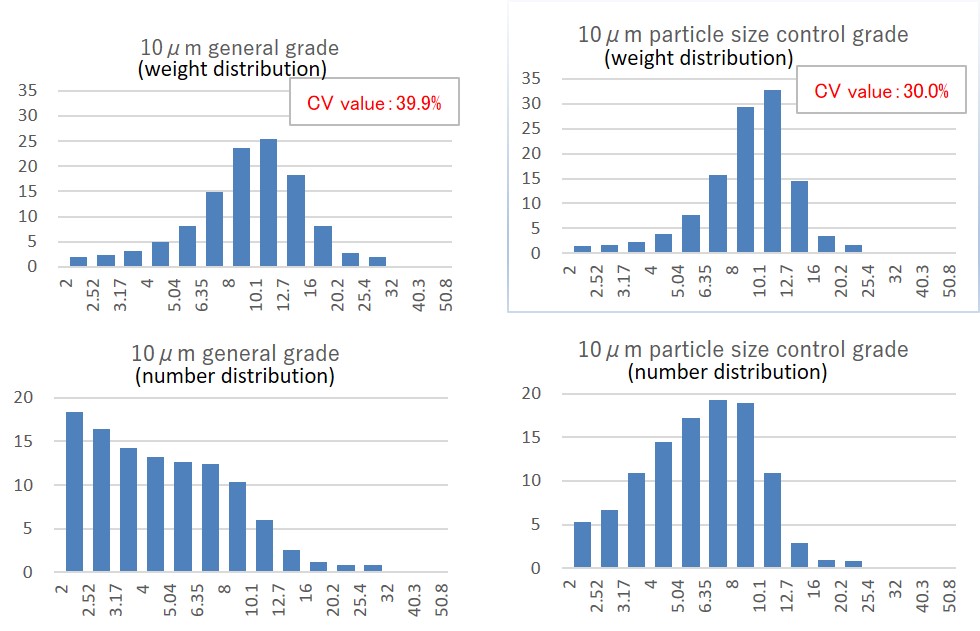
Average particle diameter and particle size distribution
- Average particle diameters can be controlled within a scope of 2 to 100 μm.
- The ratio of fine and rough particles can be adjusted.
Composition control
Changing various properties is possible through the selection of various resins and the copolymerization of acrylic monomers.
- Softness of the resin
Customers can expect improvements in terms of the feel and positive effects in terms of the prevention of abrasion. - Solvent resistance
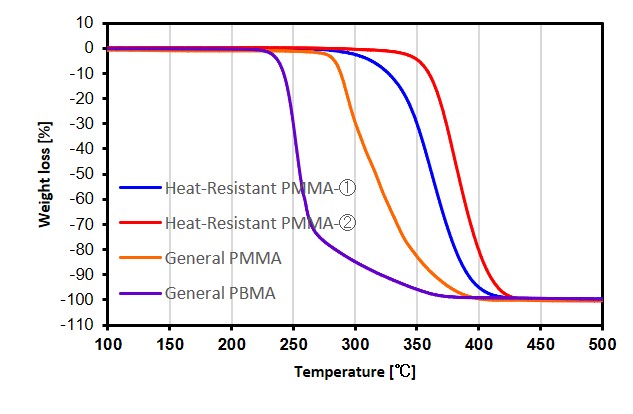
Customers can expect reductions in terms of viscosity change when adding elements to various solvents. - Heat-resistance (thermal decomposition)
By changing the resin's structure, you can change the temperature at which thermal decomposition starts.
Customers can expect reductions in terms of thermal decomposition and thermal yellowing when kneading at high temperatures.
Thermal decomposition behavior of acrylic-type fine particles
- Refractive index (1.410 to 1.590)
Control of the refractive index is possible by performing adjustments to the resin structure.
Polycarbonate resin (refractive index of 1.59): Light-diffusing fine particles 100:4
- Fine particle refractive index: 1.55
- Fine particle refractive index: 1.53
- Fine particle refractive index: 1.49
-

Sample molded board
- Modification of particle surfaces (Hydroxy group modification, carboxyl group modification, and so on)
Customers can expect improvements in terms of compatibility with matrix resins and the addition of reactivity.